8.9. Non-Bond Energy Renormalization Potential¶
8.9.1. Functional Form¶
The non-bond Energy Renormalization potential has the functional form:
\(E=\left( {{\epsilon }_{A}}-{{\epsilon }_{g}} \right)\left[ \frac{1}{1+{{e}^{-k\left( T-{{T}_{T}} \right)}}} \right]+{{\epsilon }_{g}}\)
The force-field parameters for this potential and units are given by:
| Equation Symbol | Parameter Definition | Units |
| \({\epsilon }_{A}\) | Epsilon value in Arrhenius regime | energy/mol |
| \({\epsilon }_{g}\) | Epsilon value in glassy regime | energy/mol |
| \(k\) | Temperature breadth of the transition | N/A |
| \({T}_{T}\) | Crossover point of sigmoidal function | temperature |
8.9.2. XML Schema¶
The XML schema for the non-bond Energy Renormalization potential has the following representation (design mode representation using Liquid XML Studio):
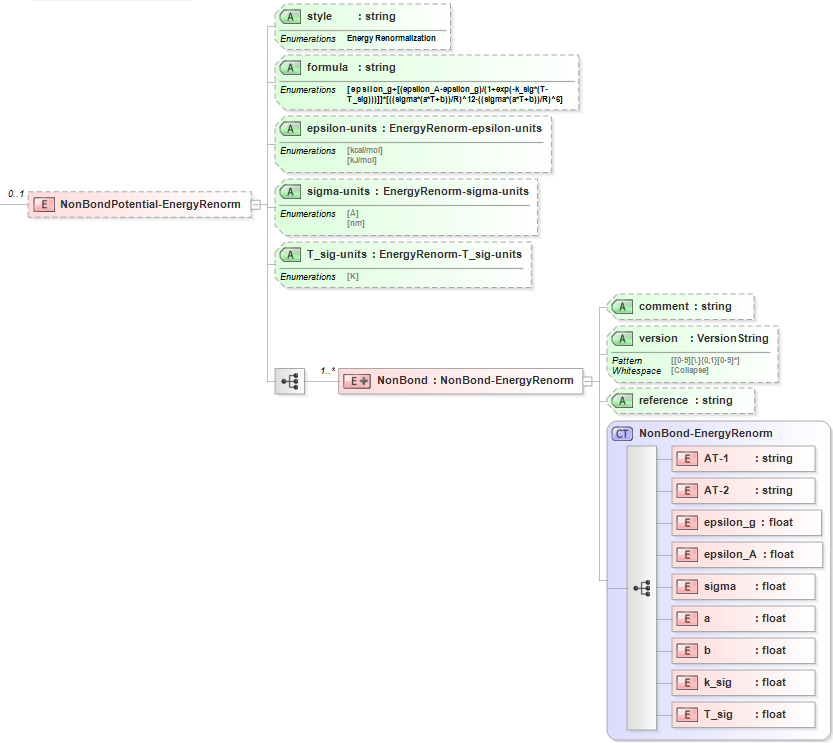
The relationship between the equation symbols and XML schema notations are given by:
| Parameter Definition | Equation Symbol | Schema Notation |
| Atom type of atom [i] | (implicit) | AT1 |
| Atom type of atom [j] | (implicit) | AT2 |
| Epsilon value in Arrhenius regime | \({\epsilon }_{A}\) | epsilon_A |
| Epsilon value in glassy regime | \({\epsilon }_{g}\) | epsilon_g |
| Temperature breadth of the transition | \(k\) | k_sig |
| Exponent of attractive term | \({\gamma }_{att}\) | n_att |
The general attributes (describing the entire data set) are given by:
| General Attributes | Cardinality | Value/Definition |
| style | Fixed | Mie |
| formula | Fixed | C*epsilon*[(sigma/R)^m_rep-(sigma/R)^n_att] |
| a_ij-units | Required | Enumerations specified in schema |
| r_c-units | Required | Enumerations specified in schema |
The specific attributes (attached to each set of parameters) are given by:
| Specific Attributes | Cardinality | Value/Definition |
| comment | Optional | Comment attached to parameter set |
| version | Optional | Version number of parameter set |
| reference | Optional | Reference attached to parameter set |
Note that an XML document will be rejected from being entered into the WebFF database if a required attribute is left unspecified.
8.9.3. References¶
- LAMMPS Mie Pair Potential.
- Liquid XML Studio.
- Wenjie Xia, Jake Song, Cheol Jeong, David D. Hsu, Frederick R. Phelan Jr., Jack F. Douglas, Sinan Keten, “Energy-Renormalization for Achieving Temperature Transferable Coarse-Graining of Polymer Dynamics,” Macromolecules, 50 (21), pp. 8787–8796, (2017). DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b01717
- Wenjie Xia, Jake Song, Nitin H. Krishnamurthy, Frederick R. Phelan Jr., Sinan Keten, Jack F. Douglas, “Energy Renormalization for Coarse-Graining the Dynamics of a Model Glass-Forming Liquid,” Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 122 (6), pp. 2040-2045, (2018). DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.8b00321
- Jake Song, David D. Hsu, Kenneth R. Shull, Frederick R. Phelan Jr., Jack F. Douglas, Wenjie Xia, Sinan Keten, “Energy Renormalization Method for the Coarse-Graining of Polymer Viscoelasticity,” Macromolecules, 51(10), pp. 3818–3827, (2018). DOI: 10.1021/acs.macromol.7b02560
- Wenjie Xia, Nitin K. Hansoge, Wen-Sheng Xu, Frederick R. Phelan Jr., Sinan Keten, and Jack F. Douglas, “Energy renormalization for coarse-graining polymers having different segmental structures,” Science Advances 5(4), eaav4683, (19 Apr 2019). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4683